
- August 25, 2023
- Dennis Frank
- 10
What is a smart contract? It’s not just some tech jargon you hear in the blockchain world.
You see, it’s something that could potentially revolutionize how we conduct business… and more.
A smart contract isn’t your typical paper agreement. Oh no, folks!
This digital marvel automates transactions without the need for an intermediary. Now that, my friends, is game-changing!
Table of Contents:
What is a Smart Contract
The Basics of Smart Contracts
In the world of blockchain and cryptocurrency, smart contracts have emerged as a revolutionary tool. But what exactly are they? Simply put, smart contracts are self-executing agreements with terms directly embedded into code lines. They exist on decentralized networks known as blockchains.
The Basics of Smart Contracts
A key objective for creating smart contracts is to simplify structuring business developments surrounding these digital pacts. By eliminating third-party involvement such as financial institutions or lawyers, we can save time while reducing potential disputes due to increased transparency.
The magic behind this technology lies in its ability to execute tasks when certain conditions are met – an idea that effectively links smart contract platforms with real-world applications.
Digital Trust Through Blockchain-Based Smart Contracts Today Means Enhanced Security
An integral part of every smart contract’s design involves utilizing blockchain technology for security purposes. Each transaction processed through these paired smart contracts gets recorded onto the blockchain ledger where it becomes unalterable — providing assurance against manipulation and fraud.
This immutability feature creates trust among participants because once agreed-upon terms get encoded into the programming language used by popular blockchains, they will be executed precisely according to plan without any possibility for tampering.
Coding Languages Used in Deploying Smart Contracts: A Closer Look
Solidity: Known primarily due to Ethereum’s pioneering role within this field.
Developed by Hyperledger Fabric.
An alternative Python-like language also supported on Ethereum.
The choice between languages often depends upon specific needs and requirements associated with each project—some may prioritize simplicity over complexity while others might need more advanced features only available from particular options.
Dive into the world of #blockchain. Smart contracts are revolutionizing business models by providing transparent, secure agreements that execute tasks when conditions are met. Say goodbye to third-party disputes and hello to enhanced security. #SmartContracts #CryptocurrencyClick to Tweet
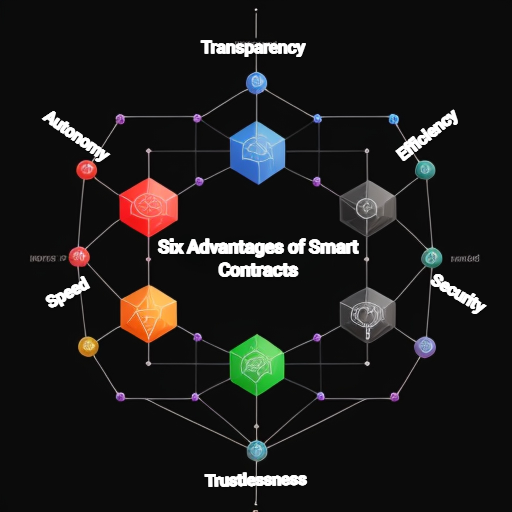
Advantages of Smart Contracts
The digital world is rapidly progressing, and smart contracts are becoming increasingly popular. But what exactly are these? And more importantly, how do they benefit us?
In essence, smart contracts provide several key advantages over traditional contract methods.
Automation: The New Norm
A primary advantage offered by blockchain-based smart contracts today means you can enjoy automated execution once conditions specified within the contract have been met. This effectively eliminates intermediaries such as legal firms or notaries – reducing costs while increasing efficiency.
This accommodation for automatic transaction handling simplifies structuring smart contracts to meet various business developments surrounding their usage. As a result, businesses can save time without compromising on security or reliability when executing agreements.
Precision Matters: Ensuring Accuracy with Smart Contracts
Explains why precision matters.
-
- Digital agreement platforms like Ethereum ensure every detail must be explicitly defined before it functions.
-
- As everything operates under pre-set rules within popular blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum, this guarantees each party will adhere to its obligations, thereby enhancing trust among stakeholders involved in any given deal.
Savings from Reduced Intermediation Costs
Highlights potential savings through reduced intermediation costs.
-
- Cutting out middlemen streamlines complex procedures associated with contractual obligations, saving both money and effort required to manage them manually.
-
- Note: Increased efficiency translates into lower operational costs, which ultimately benefits end-users who may see reduced fees associated with services rendered via these platforms.
Dive into the future with smart contracts. They’re automating transactions, slashing costs by cutting out middlemen, and ensuring accuracy in every deal. The digital world is evolving – don’t get left behind. #Blockchain #SmartContractsClick to Tweet
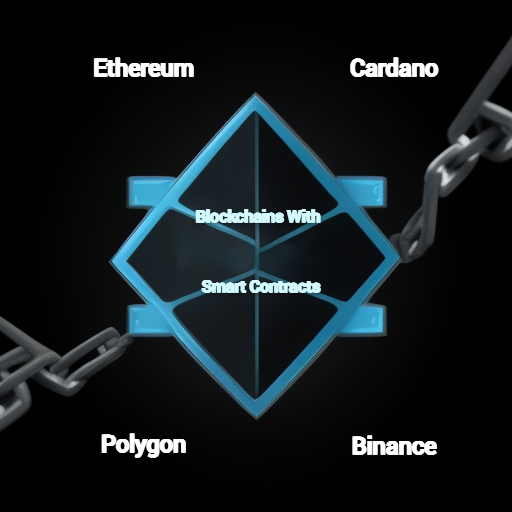
Blockchains with Smart Contracts
In the vast and rapidly evolving world of blockchain technology, several platforms have made significant strides in implementing smart contracts. Let’s explore some key players that accommodate smart contracts.
Ethereum: The Pioneer
Ethereum, a popular blockchain platform, has been instrumental in shaping business developments surrounding smart contracts. Ethereum was specifically built to effectively link smart contracts and applications using its native currency – Ether.
The use of a Turing-complete programming language on this platform allows developers to simplify structuring complex codes for their paired smart contracts leading to sophisticated decentralized apps (DApps).
Cardano: Research First Approach
Moving forward we encounter Cardano. This unique contender focuses heavily on research-first driven methods when it comes down to deploying its own version of blockchain-based smart contract technology.
This scientific approach aims at reducing errors during development while enhancing security within Cardano’s ecosystem by applying formal verification techniques ensuring all conditions satisfy common contractual conditions before execution begins.
Polygon (Matic): Scalability Focus
Aiming towards scalability is Polygon (formerly Matic Network). Offering robust solutions through interoperable networks which can support high-performance DApps swiftly while providing an environment compatible with Ethereum’s Virtual Machine (EVM) makes Polygon stand out among others.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC): Speed & Low Fees
Binance Smart Chain (BSC), operating parallelly alongside Binance’s original chain but offering additional features like compatibility with EVM along with faster transactions at reduced costs, making it appealing for DeFi (Video) projects as well as other DApp developers seeking cost-effective yet secure alternatives.
Each one brings something different onto the table when talking about executing safe, efficient automated digital agreements also known as “smart contracts”. As you further delve into the cryptocurrency realm, understanding how these diverse platforms utilize this revolutionary tool will be a crucial part of choosing where your interests lie best.
Key Takeaway:
Smart contracts are reshaping the blockchain landscape with platforms like Ethereum pioneering, Cardano using a research-first approach, Polygon focusing on scalability, and Binance Smart Chain offering speed and low fees. Understanding these diverse offerings is key to navigating the cryptocurrency realm effectively.
Smart Contract Security
The world of smart contracts technology is exciting, but it’s not without its share of potential threats. However, fear not. There are steps taken to make sure that these digital arrangements remain secure and reliable.
Let’s dive into how we can effectively link smart contracts with security protocols to keep them safe from malicious attacks.
Auditing Services for Smart Contracts
You might be wondering: How do you secure a contract that exists solely on the blockchain? The answer lies within auditing services. These companies specialize in examining code before it becomes part of the network. Certik and Quantstamp are two such firms who play watchdog over your precious lines of programming language. This process helps detect any vulnerabilities which could potentially harm or disrupt business models based around blockchain-based smart contracts. Today, securing their codes first means securing their business models.
Note: Audits aren’t just a one-time thing – they’re an ongoing process that ensures continuous protection against new threats as well.
Potential Threats Against Smart Contracts
No system is foolproof – even ones built upon popular blockchains like Ethereum have seen breaches occur due to loopholes being exploited by hackers. Remember “The DAO” attack? This serves as our cautionary tale.
-
- To combat this, developers often use patterns known as Checks-Effects-Interactions (CEI). It enforces proper sequencing within functions and prevents reentrancy attacks where attackers call back repeatedly into function before previous invocations complete execution.
-
- In addition, employing micropayments automatically through paired smart contracts also reduces risk exposure by limiting transaction value at each instance.
-
- Last but certainly not least, there are tools available designed specifically for testing every line under different scenarios ensuring robustness prior deployment onto networks like Truffle Suite or Ganache CLI.
In today’s digital age, the security of online transactions and data is paramount. With the rise of blockchain technology and smart contracts, there’s a growing need to ensure these contracts are not only efficient but also secure from potential threats.
Enter Artificial Intelligence (AI). AI plays a pivotal role in enhancing the security of smart contracts. It continuously monitors and analyzes patterns to detect any anomalies or potential breaches. By learning from past incidents and predicting future threats, AI provides an additional layer of protection, ensuring that smart contracts remain tamper-proof. For a deeper dive into this topic, consider Exploring the Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Smart Contracts.
This article sheds light on the myriad ways AI is revolutionizing the world of smart contracts and ensuring a safer digital transaction environment.
But remember: Even though best practices can mitigate risks associated with deploying smart contracts on platforms accommodating them, vigilance post-deployment remains essential because new vulnerabilities may emerge over time. Always stay updated.
Key Takeaway:
In the thrilling but perilous world of smart contracts, safety is key. Auditing services like Certik and Quantstamp act as guardians, scrutinizing code for vulnerabilities. But don’t rest easy yet – even with best practices in place, continuous vigilance post-deployment is crucial to combat emerging threats. Stay sharp.
FAQs in Relation to What is a Smart Contract
What is a smart contract in simple terms?
A smart contract is a self-executing agreement with the terms of the deal directly written into lines of code. It automatically enforces and executes transactions without intermediaries.
What are smart contracts explained with examples?
An example of a smart contract could be an insurance policy that pays out when specific conditions are met, like weather-related flight cancellations. The payout happens automatically based on data input, no claims needed.
What are smart contracts and why are they useful?
Smart contracts automate transactions securely and transparently. They reduce human error, cut costs by eliminating middlemen, increase speed through automation, and enhance trust as execution is managed by impartial network nodes.
How does the author describe smart contracts?
The author describes them as digital agreements programmed to execute or enforce themselves upon meeting certain conditions. They streamline processes while enhancing security within blockchain networks.
Conclusion
Smart contracts are a revolution in the world of business transactions.
They’re not your typical paper agreements, but digital marvels that automate processes without needing an intermediary.
The advantages they offer over traditional contracts are numerous and significant, including increased efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced trust among parties involved.
Different blockchains have implemented smart contracts to leverage these benefits.
But with great power comes great responsibility – ensuring their security is paramount for maintaining integrity and safety.
If you’ve found this exploration into smart contracts intriguing, there’s so much more to discover in the fascinating realm of cryptocurrency and blockchain technology. Whether you’re a beginner or looking to deepen your knowledge further, Coinbeat.co is here as your guide on this journey. Dive deeper, explore more about blockchain technology at KryptoKraken.com!
































































10 comments on “What is a Smart Contract?”